| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 카카오프로젝트 100
- 깃허브
- ES6
- javascript
- 카카오프로젝트
- python
- 보안뉴스
- 보안뉴스요약
- 다크웹
- 자바스크립트 객체
- 자바스크립트 기본 문법
- oracle db
- 자바스크립트 jQuery
- numpy
- 자바스크립트 API
- 자바스크립트 node
- oracle
- php
- 보안뉴스한줄요약
- 자바스크립트 element api
- 자바스크립트 prototype
- 파이썬
- 오라클
- 카카오프로젝트100
- 보안뉴스 한줄요약
- 랜섬웨어
- GIT
- Oracle SQL
- 보안뉴스 요약
- 자바스크립트
- Today
- Total
FU11M00N
[LeetCode] Linked List Cycle - Javascript 본문
Linked List Cycle
[순환 노드 찾기]
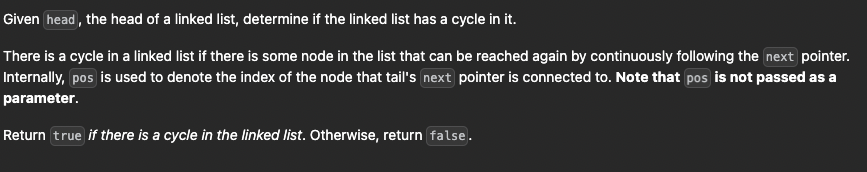
제약 조건
The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 10^4].
-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Example

ex1) Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
ex2) Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
ex3) Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.초기 문제 접근 방식

[3,2,0, -4] -> [null, 2,0, -4] -> [null, null, 0, -4] -> [null, null, null,-4] -> [null, null, null, null] -> -4는 2번 노드를 가리키고 있지만, 2번 노드는 null 값이 되었기에 해당 값이 null이라면 사이클이 있는 것으로 판단하면 된다.
문제를 풀 때 문제 자체가 어렵다기보단 주어진 연결 리스트를 어떻게 접근하는지 몰라 시간을 많이 소비했다.
우선 head가 주어지니, head.val을 통해 head가 가리키는 node의 값에 접근할 수 있다.
while 문을 사용해 head가 node를 가리 켤 때까지 반복문을 사용하고,
제어문을 사용해 head.val의 값이 없을 때까지 즉 노드의 값이 없다면 true를 리턴한다.
아니라면 head.val에는 null 값을 넣고 head가 다음 노드를 가리키게 head.next를 head 값에 넣는다.
전체코드
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function (head) {
while (head) {
if (!head.val) {
return true
}
head.val = null;
head = head.next
}
return false
};
다른 solve 코드
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasCycle = function (head) {
if (head === null) {
return false;
}
let rabbit = head.next;
let turtle = head;
while (rabbit !== null) {
if (rabbit === turtle) {
return true;
}
if (rabbit.next) {
rabbit = rabbit.next.next;
turtle = turtle.next;
continue;
}
break;
}
return false;
};플로이드의 순환 알고리즘은
하나의 포인터는 두 칸을 움직이게 하고, 하나의 포인터는 한 칸을 움직이게 한다.
이 두 개의 포인터는 언젠가 만나게 된다.(단, 순환구조일 경우)
rabbit과 turtle 변수를 생성해 rabbit은 head가 두 번째 노드를 가리키게 하고
turtle은 현재 head가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키게 한다.
만약 rabbit과 turtle 이 같은 노드를 가리킨다면 true를 반환한다.
while을 사용해 rabbit이 null이 아닐 때까지 반복문을 수행하고,
만약 rabbit.next의 값이 존재한다면 rabbit에는 rabbit.next.next를 해 node를 두 칸 이동할 수 있는지 판단하고
turtle에는 turtle.next 다음 노드를 가리키게 한다.
바로 rabbit.next.next를 가리키게 하지 않는 이유는 만약 두 칸 뒤에 노드가 없다면 null 에러가 발생하기에 한 칸 뒤의 노드가 있는지 확인한 후. next.next를 해야 에러를 방지할 수 있다.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] Add Two Numbers - Javascript (2) | 2023.08.28 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] Merge Two Sorted Lists - Javascript (0) | 2023.08.28 |
| [LeetCode] Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters - Javascript (0) | 2023.08.28 |
| [LeetCode] Minimum Size Subarray Sum - Javascript (1) | 2023.08.27 |
| [LeetCode] Two Sum II - Input Array Is Sorted - Javascript (0) | 2023.08.27 |




